Executive Summary
ClickFix is a rapidly evolving social engineering technique that began gaining momentum in mid-2024. We have observed the exploitation of this social engineering tactic within multiple client environments as well as multiple threat intelligence sources. By camouflaging malware delivery within fake CAPTCHA verification screens or error messages, threat actors successfully lure end users into pressing Windows+R, pasting malicious code, and executing it, often without raising immediate suspicion. This method of tricking people into self-instigating the infection pathway sidesteps many traditional security controls. This advisory examines how ClickFix operates, documents active campaigns, and provides detection strategies and mitigation recommendations.
What is ClickFix?
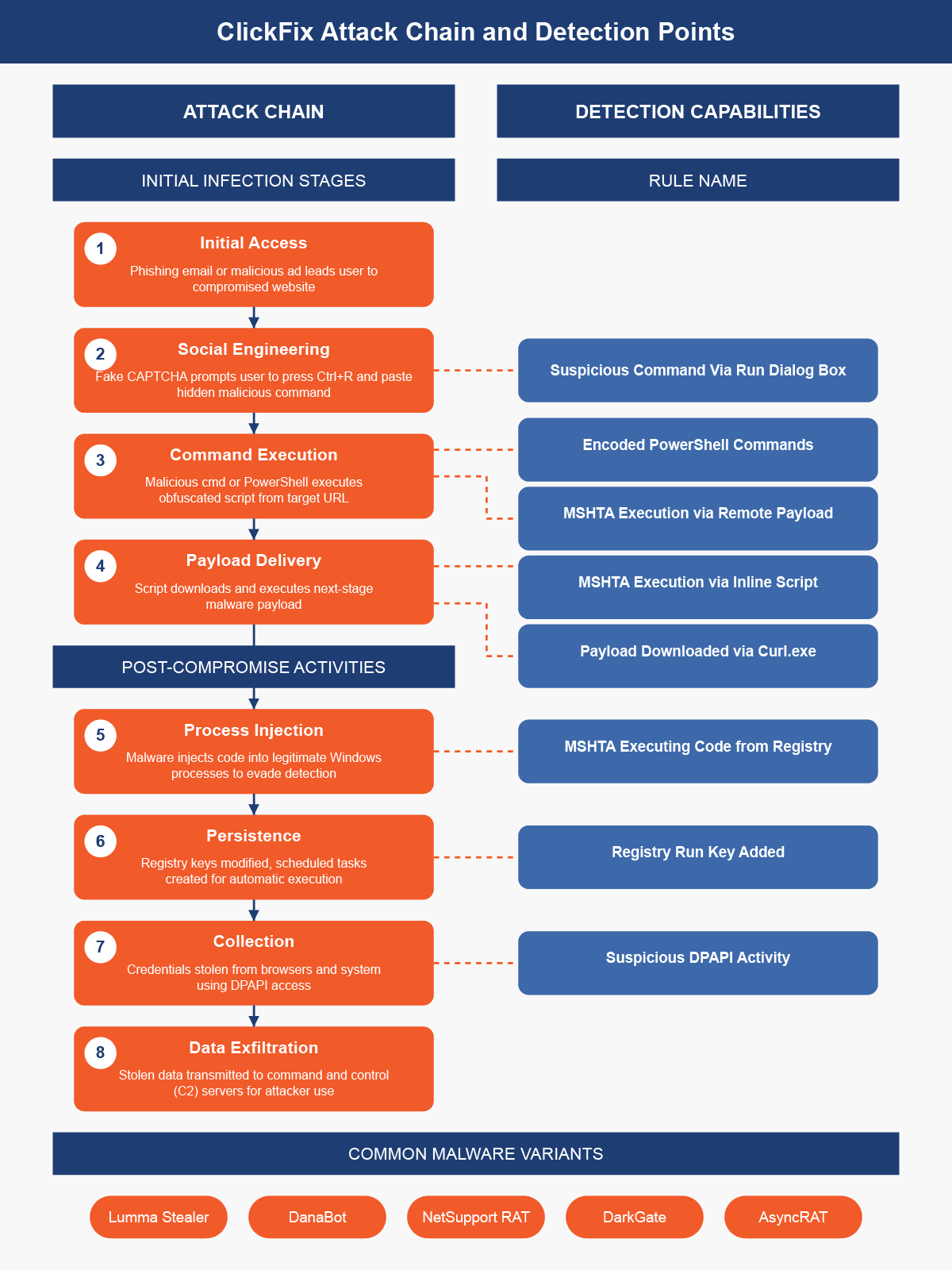
ClickFix is a social engineering tactic that tricks users into executing malicious code through a series of deceptive prompts. The attack typically begins with the following sequence:
1. Initial Engagement
Users are presented with a fake CAPTCHA verification screen or error message when visiting compromised websites, clicking on malicious ads, or opening phishing attachments.

Fake CAPTCHA – Medium.com (Rizqi Setyo Kusprihantanto)
2. Social Engineering:
The fake verification page instructs the user to perform a specific sequence of actions:
- Press Windows+R to open the Run dialog
- Press Ctrl+V to paste content from clipboard (which contains malicious code secretly copied by the webpage)
- Press Enter to execute the command
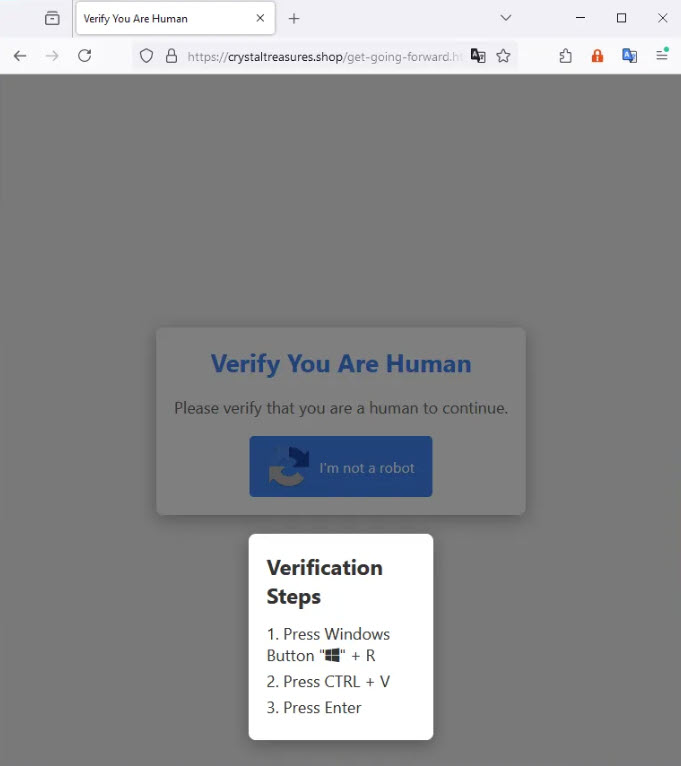
Fake Verification Page – Medium.com (Rizqi Setyo Kusprihantanto)
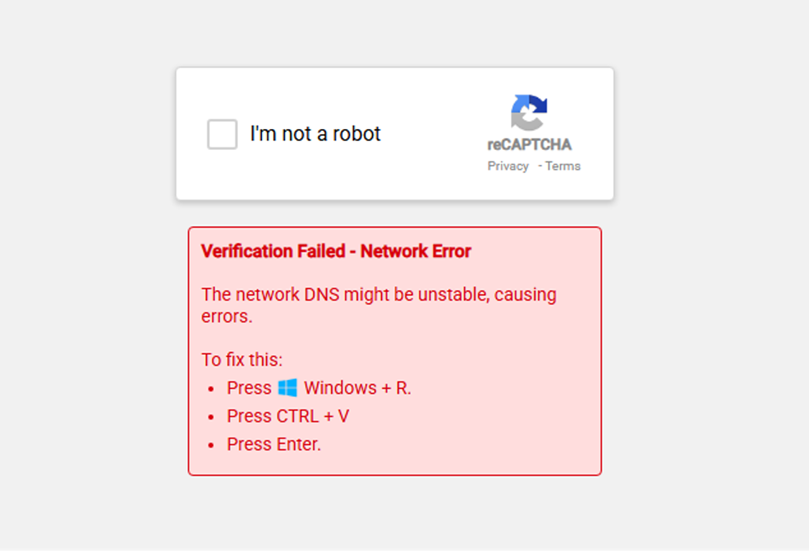
Fake Verification Page – (Ben Martin)
3. Execution
The pasted command typically leverages Windows utilities like mshta.exe or PowerShell to download and execute additional malicious payloads.
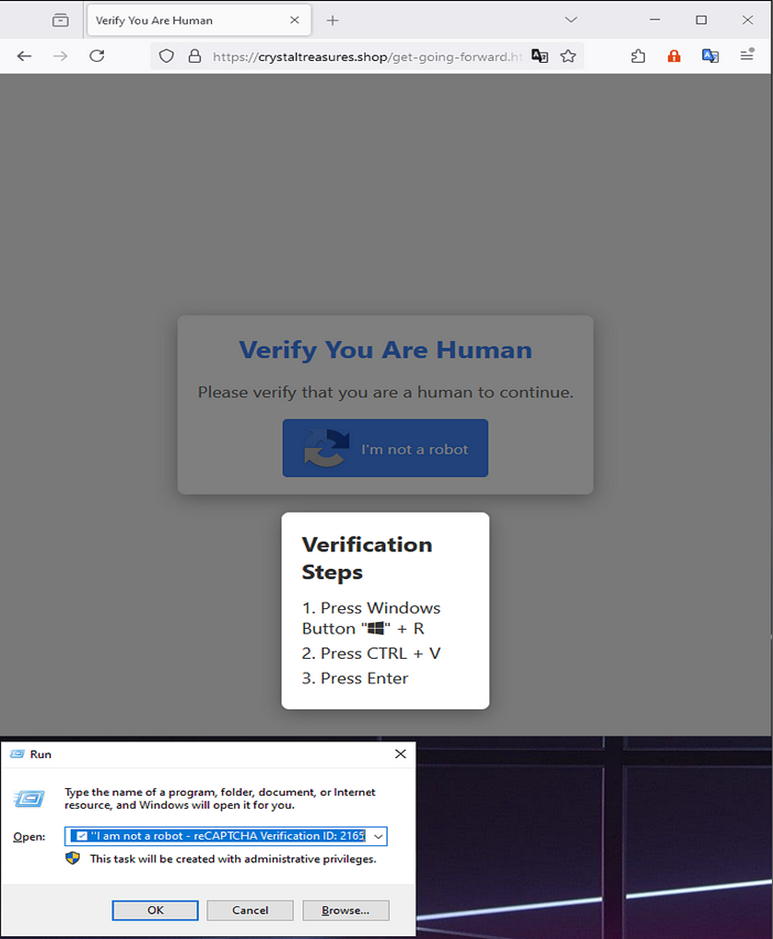
Fake Verification Page – Medium.com (Rizqi Setyo Kusprihantanto)
Active ClickFix Campaigns
Several major malware families have been distributed through ClickFix campaigns. Lumma Stealer, a Malware-as-a-Service infostealer that emerged in 2022, has been widely deployed through these campaigns since December 2024. The Center for Internet Security (CIS) identified a campaign specifically targeting U.S. State, Local, Tribal, and Territorial (SLTT) government organizations with Lumma Stealer. Other prominent malware distributed via ClickFix includes NetSupport RAT (documented by eSentire since January 2025), AsyncRAT, VenomRAT, DanaBot, XWorm, DarkGate, and various ransomware payloads. These malware families collectively provide attackers with capabilities ranging from credential theft and cryptocurrency wallet compromise to remote system control and data exfiltration.
In the past few months alone, various sources have reported widespread ClickFix abuse. Trustwave SpiderLabs observed multi-stage PowerShell execution processes with XOR encryption and AMSI bypasses to deliver multiple infostealer variants. FortiGuard Labs documented a phishing campaign using ClickFix to deploy a modified Havoc C2 Framework that leverages Microsoft Graph API to obscure communications. Sucuri research identified a massive WordPress-based campaign affecting over 5,200 websites, which used the Binance Smart Chain network to load malicious JavaScript that creates fake CAPTCHA screens. Researchers observed prominent threat group, Lazarus leveraging the ClickFix tactic to distribute FrostyFerret , GolangGhost, and other malware. Notably in Lazarus’s campaign curl was leveraged in place of mshta to deliver payloads. Microsoft Security researchers documented a campaign impersonating Booking.com that targeted the hospitality sector with multiple credential-stealing malware variants. According to Microsoft Threat Intelligence, these campaigns target individuals across multiple sectors, including hospitality, healthcare, banking, telecom, and marketing organizations in North America, Europe, Oceania, and parts of Asia.
Recommendations
Mitigations
Group Policy Object (GPO) Controls:
- Apply group policy restrictions that disable or restrict the usage of the Windows+R functionality, preventing users from easily accessing the Run dialog that ClickFix attacks rely on.
- Restrict WScript.exe and mshta.exe usage via AppLocker GPO or Windows Defender Application Control (WDAC).
Tools/EDR:
- Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA) solution software such as Appgate SDP can be used if restricting the Windows Run dialog is not preferable. Such software can be configured and used as a “speedbump”, warning users of potential malicious Windows Run executions.
User Education:
- CAPTCHA Awareness: Educate users specifically about ClickFix tactics, emphasizing that legitimate CAPTCHA verifications never require executing Windows commands and that they should report suspicious verification prompts requesting Windows+R key combinations to security teams.
- Reporting Procedures: Establish clear procedures that encourage users to report suspicious websites or unusual CAPTCHA experiences.
Detection Opportunities
- Monitor for and consider blocking JavaScript or VBScript from launching downloaded executable content.
- Develop detection rules for process chains involving mshta.exe or PowerShell executing with encoded parameters, especially when following browser activity.
- Monitor for suspicious RunMRU registry entries containing PowerShell commands, particularly those with base64 encoding or invoking web requests.
- Consider implementing detections for AMSI bypass techniques, especially code patterns containing strings like “AMSI_RESULT_NOT_DETECTED,” which sources note is used by Lumma Stealer and other ClickFix-distributed malware.
Safeguards for SCALR XDR Customers
SRA’s Detection Engineering team is regularly adding new detections. This is intended to highlight potential safeguards observed in the common attack chain and may not be exhaustive of full protection.
SCALR XDR customers are protected by the following detection rules:
Alert |
Prerequisites |
Description |
| Potentially Suspicious Command Executed Via Run Dialog Box |
Necessary Logs: Registry Events Compatible EDR(s): |
MITRE Technique: T1202: Indirect Command Execution This alert looks for new MRU Registry entries where the values are related to CMD, PowerShell, or MSHTA commands being run. An adversary could execute malicious commands using the Run Dialog Box. The Windows Run Dialog box allows users to open programs, websites, and access Windows settings. The user will copy and paste a command into the Run Dialog box and execute it. This gives the attacker the initial foothold on the endpoint. |
| MSHTA Execution via Remote Payload |
Necessary Logs: Process Creation Events Compatible EDR(s): Microsoft Defender CrowdStrike SentinelOne |
MITRE Technique: T1218.005: Mshta This alert will fire when mshta executes a remote file using either http or ftp. Threat actors can use mshta.exe, which is a trusted Windows utility, to covertly download and/or execute malicious files to bypass application control solutions. |
|
Registry Run Key Added
|
Necessary Logs: Process Creation Events Compatible EDR(s): Microsoft Defender CrowdStrike SentinelOne |
MITRE Technique: T1547.001: Registry Run Keys / Startup Folder This alert detects a new Registry run key being added. Adversaries may add a run key in order to establish persistence on a system. |
|
MSHTA Execution via Inline Script
|
Necessary Logs: Process Creation Events Compatible EDR(s): Microsoft Defender CrowdStrike SentinelOne |
MITRE Technique: T1218.005: System Binary Proxy Execution: Mshta This detection triggers when MSHTA.exe is used to execute JavaScript or VBscript. Adversaries may abuse mshta.exe to proxy execution of malicious .hta files and Javascript or VBScript through a trusted Windows utility. |
| Payload Downloaded via Curl.exe |
Necessary Logs: Process Creation Events Compatible EDR(s): Microsoft Defender CrowdStrike SentinelOne |
MITRE Technique: T1105: Ingress Tool Transfer Curl is a command-line tool to transfer data to or from a server, using any of the supported protocols: TTP, FTP, IMAP, POP3, SCP, SFTP, SMTP, TFTP, TELNET, LDAP, or FILE. Curl.exe has increasingly been used by adversaries as part of their attacks to download malicious payloads onto infected systems. This is typically achieved by using the -o switch, which saves the downloaded file on the local machine with the name provided in the parameters, and by defining a URL, which is where the malicious artifact resides. |
| MSHTA Executing Code from Registry |
Necessary Logs: Process Creation Events Compatible EDR(s): Microsoft Defender CrowdStrike SentinelOne |
T1218.005: Mshta This alert detects Mshta executing code from the registry. Adversaries may store code in the Registry as part of initial access that can then be executed via mshta commands. |
| Suspicious Encoded PowerShell Commands |
Necessary Logs: Process Creation Events Compatible EDR(s): Microsoft Defender SentinelOne
|
T1027: Obfuscated Files or Information This rule is designed to detect the execution of encoded PowerShell commands, which are often used by attackers to obfuscate malicious activities. Encoding PowerShell commands is a common technique to bypass security controls and evade detection. This rule aims to identify and flag such activities to prevent potential security breaches. |
Potentially Suspicious Command Executed Via Run Dialog Box
PrerequisitesNecessary Logs: Registry Events Compatible EDR(s): |
DescriptionMITRE Technique: T1202: Indirect Command Execution This alert looks for new MRU Registry entries where the values are related to CMD, PowerShell, or MSHTA commands being run. An adversary could execute malicious commands using the Run Dialog Box. The Windows Run Dialog box allows users to open programs, websites, and access Windows settings. The user will copy and paste a command into the Run Dialog box and execute it. This gives the attacker the initial foothold on the endpoint. |
MSHTA Execution via Remote Payload
PrerequisitesNecessary Logs: Process Creation Events Compatible EDR(s): |
DescriptionMITRE Technique: T1218.005: Mshta This alert will fire when mshta executes a remote file using either http or ftp. Threat actors can use mshta.exe, which is a trusted Windows utility, to covertly download and/or execute malicious files to bypass application control solutions. |
Registry Run Key Added
PrerequisitesNecessary Logs: Process Creation Events Compatible EDR(s): |
DescriptionMITRE Technique: T1547.001: Registry Run Keys / Startup Folder This alert detects a new Registry run key being added. Adversaries may add a run key in order to establish persistence on a system. |
MSHTA Execution via Inline Script
PrerequisitesNecessary Logs: Process Creation Events Compatible EDR(s): |
DescriptionMITRE Technique: T1218.005: System Binary Proxy Execution: Mshta This detection triggers when MSHTA.exe is used to execute JavaScript or VBscript. Adversaries may abuse mshta.exe to proxy execution of malicious .hta files and Javascript or VBScript through a trusted Windows utility. |
Payload Downloaded via Curl.exe
PrerequisitesNecessary Logs: Process Creation Events Compatible EDR(s): |
DescriptionMITRE Technique: T1105: Ingress Tool Transfer Curl is a command-line tool to transfer data to or from a server, using any of the supported protocols: TTP, FTP, IMAP, POP3, SCP, SFTP, SMTP, TFTP, TELNET, LDAP, or FILE. Curl.exe has increasingly been used by adversaries as part of their attacks to download malicious payloads onto infected systems. This is typically achieved by using the -o switch, which saves the downloaded file on the local machine with the name provided in the parameters, and by defining a URL, which is where the malicious artifact resides. |
MSHTA Executing Code from Registry
PrerequisitesNecessary Logs: Process Creation Events Compatible EDR(s): |
DescriptionMITRE Technique: T1218.005: Mshta This alert detects Mshta executing code from the registry. Adversaries may store code in the Registry as part of initial access that can then be executed via mshta commands. |
MSHTA Execution via Inline Script
PrerequisitesNecessary Logs: Process Creation Events Compatible EDR(s): |
DescriptionMITRE Technique: T1218.005: System Binary Proxy Execution: Mshta This detection triggers when MSHTA.exe is used to execute JavaScript or VBscript. Adversaries may abuse mshta.exe to proxy execution of malicious .hta files and Javascript or VBScript through a trusted Windows utility. |






